Dose
 scroll scroll 
Measure of a radiation effect to be indicated more
precisely. The absorbed dose indicates the total radiation energy absorbed
by the irradiated matter in gray (Gy). Central dose variables in radiation
protection are "organ dose" and "effective dose".
The term "body dose" is used as a collective term for organ
dose and effective dose. The latter two are protective variables in
radiation protection, including risk assessment. They form a basis for
the assessment of the probability of stochastic radiation effects for
absorbed doses far below the thresholds for deterministic radiation
damage. The unit of these dose values is sievert, symbol: Sv.
The Radiological Protection Ordinance requires measurement
of the personal dose for the determination of the body dose which cannot
be measured directly. Personal dose is the dose equivalent measured
in the measuring variables of depth dose and skin dose at an area of
the body surface representative of radiation exposure. The depth dose Hp(10) in this case is an estimated value for
the effective dose for whole body exposure with penetrating radiation
and the organ doses of deep organs and the skin dose Hp(0,07)
are an estimated value for the skin dose.
The dose variables used in radiation protection in more detail:
-
Dose equivalent
The dose equivalent is the product of the absorbed dose in ICRU
(see 'Soft tissue' and 'Quality
factor'). In the case of several radiation types and radiation
energies the total dose equivalent is the sum of its determined
individual amounts. The unit of the dose equivalent is Sievert.
-
Effective dose
The effective dose is the suitable variable to indicate a uniform
dose value in case of different exposure of various body parts in
order to evaluate the risk of late radiation injuries. The effective
dose E is the sum of the average organ
doses HT in the individual organs and
tissues of the body due to external or internal radiation exposure
multiplied by the tissue weighting factors WT.
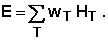
-
Organ |
Tissue weighting factor wT |
Gonads |
0.20 |
Colon |
0.12 |
Bone marrow (red) |
0.12 |
Lung |
0.12 |
Stomach |
0.12 |
Bladder |
0.05 |
Chest |
0.05 |
Liver |
0.05 |
Thyroid gland |
0.05 |
Oesophagus |
0.05 |
Skin |
0.01 |
Bone surface |
0.01 |
Pancreas, small intestine, uterus, brain, spleen, muscle,
suprarenal gland, kidney, thymus gland |
0.05 |
-
Abbsorbed dose
The absorbed dose D is the quotient from the average energy transferred
to the matter in a volume element by ionizing radiation and the
mass of the matter in this volume element:
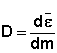
The unit of the absorbed dose is joule divided by
kilogram (J·kg-1) and its special unit name is gray
(Gy). The former unit name was rad (symbol: rd or rad).1 Gy = 100
rd; 1 rd = 1/100 Gy.
-
Committed dose
The irradiation of tissue or organs by incorporated radionuclides
is distributed over the incorporation period. This period depends
upon the physical half-life and the biokinetic behaviour of the
radionuclide. The committed dose is the time integral of the dose
rate in a tissue or organ over time. The organ committed dose HT( )
for incorporation at time t0 is the time integral of the organ dose
rate in the tissue or organ T. If no integration period is indicated,
a period )
for incorporation at time t0 is the time integral of the organ dose
rate in the tissue or organ T. If no integration period is indicated,
a period  of 50 years for adults and the period from the respective age to
the age of 70 years for children are used as a basis: of 50 years for adults and the period from the respective age to
the age of 70 years for children are used as a basis:

-
Skin dose
The skin dose Hp(0.07) is the dose equivalent
in 0.07 mm depth in the body at the application point of the personal
dosimeter.
Organ dose
-
Equivalent dose
The equivalent dose HT,R is the product of the
organ absorbed dose DT,R averaged over the
tissue/organ T generated by the radiation R and the radiation weighting
factor WR.
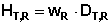
If the radiation consists of types and energies with different WR values, the individual values are added.
Radiation type and energy range |
Radiation weighting factor WR |
Photons, all energies |
1 |
Electrons and muons, all energies |
1 |
Neutrons: |
|
< 10 keV |
|
10 keV to 100 keV |
|
>100 keV to 2 MeV |
|
>2 MeV to 20 MeV |
10 |
> 20 MeV |
|
Protons, except for recoil protons, > 2 MeV |
|
Alpha particles, fission fragments, heavy
nuclei |
20 |
Radiation weighting factor
-
Local dose
The local dose is the dose equivalent for soft tissue measured at
a certain point. The local dose in the case of penetrating radiation
is the ambient dose equivalent; the local dose for radiation with
low penetration depth is the directional dose equivalent. The local
dose in the case of penetrating radiation is an estimated value
for the effective dose and the organ doses of deep organs for radiation
with low penetration depth is an estimated value for the skin dose
of a person at the place of measurement.
-
Personal dose
The Radiological Protection Ordinance requires measurement of the
personal dose for determination of the body dose. The personal dose
is the dose equivalent measured in the measuring variables of depth
dose and skin dose at a spot representative of radiation exposure
at the body surface. The depth personal dose in the case of whole
body exposure to penetrating radiation is an estimated value for
the effective dose and the organ doses of deep organs and the skin
dose an estimated value for the skin dose.
-
Directional dose equivalent
The directional dose equivalent H'(0.07,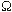 )
at the point of interest in the actual radiation field is the dose
equivalent which would be generated in the associated expanded radiation
field at a depth of 0.07 mm on the radius of the ICRU sphere (see
'ICRU sphere') which is oriented in
the fixed direction )
at the point of interest in the actual radiation field is the dose
equivalent which would be generated in the associated expanded radiation
field at a depth of 0.07 mm on the radius of the ICRU sphere (see
'ICRU sphere') which is oriented in
the fixed direction  . .
-
Depth dose
The depth dose Hp(10) is the dose equivalent
at a body depth of 10 mm at the point of application of the personal
dosimeter.
-
Personal dose equivalent
The personal dose equivalent H*(10) at the point of interest in the
actual radiation field is the dose equivalent which would be generated
in the associated oriented and expanded radiation field at a depth
of 10 mm on the radius of the ICRU sphere which is oriented opposite
to the direction of incident radiation.
back
|
|

11 - 15 March 2018
Munich, Germany

30 September - 04 October 2018
Prague, Czech Republic |