Nuclear energy
 scroll scroll
Inner binding energy of atomic nuclei. The nuclear
building blocks show various degrees of mutual binding from one atom
type to another. The maximum binding energy per nuclear building block
is within the range of the mass number 60. By means of nucleus conversion,
energy can therefore be obtained either by fission of heavy nuclei such
as uranium or by fusion of lighter nuclei such as hydrogen. The fission
of 1 kg U-235 supplies about 23 million kWh, during the fusion of deuterium
and tritium (DT-reaction) to 1 kg helium, energy of about 120 million
kWh is released. In contrast, the combustion of 1 kg coal supplies only
about 10 kWh. (See 'fusion' and 'nuclear
fission'.)
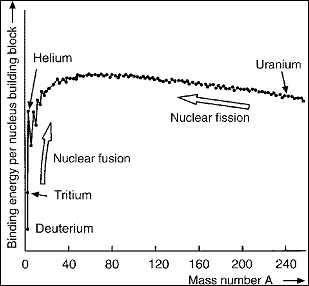
Nuclear binding energy depending on the mass number of
the nucleus of the atom
back
|
|

11 - 15 March 2018
Munich, Germany

30 September - 04 October 2018
Prague, Czech Republic |