Radiation exposure, cosmic
 scroll scroll 
The radiation reaching the earth from space is mostly of galactic and only partly of solar origin. It is very rich in energy. This primary cosmic radiation mainly consists of protons. Due to different interaction processes in the outer layers of the atmosphere new radiation groups are generated - photons, electrons, positrons, neutrons and myons. The first radiation types form the „soft“ secondary cosmic ray component, the myons the penetrating „hard" secondary cosmic ray component which can even be detected in deep mines. The influence of the magnetic field of the earth on the primary cosmic radiation results in a dependence of the secondary cosmic radiation on the geomagnetic width. The intensity of the cosmic radiation depends extensively on the altitude above sea level, since part of the radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere. Taking all components of cosmic radiation into account, this results in an annual radiation exposure of 0.3 mSv at sea level.
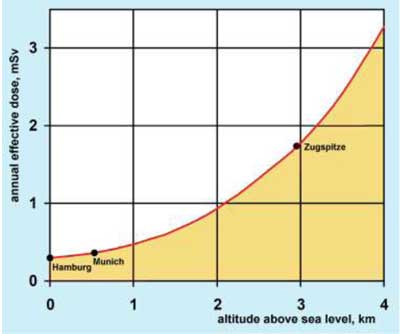
Cosmic radiation exposure as a function of altitude, latitude 50° north
back
|
|
ENS conferences |
| |
 |
TopSafe 2017
12-16 Feb. 2017
Vienna, Austria |
 |
PIME 2017
19 - 22 March 2017, Middelburg Netherlands |
 |
RRFM 2017
14 - 18 May 2017 in Rotterdam, Netherlands |
 |
ETRAP 2017
30 May - 2 June 2017, Valencia, Spain |
|
|