Steam bubble coefficient
 scroll scroll 
The reactivity of
a reactor - a measure for the deviation of the chain reaction rate from
the stable state of equilibrium - depends upon a number of operating
parameters, in a boiling water reactor, among others, on the steam bubble
contents in the coolant in the core zone. In the case of an increase
in the chain reaction rate and the resulting power and temperature increase,
a negative steam bubble coefficient has the effect that the power is
automatically limited by the growing steam bubble contents and thus
declines. In the German licensing procedure it must be verified that
the steam bubble coefficient is always negative. In the Russian RBMK reactor type the steam bubble coefficient is positive; therefore, a
power and temperature increase causes an increasingly faster chain reaction
rate, entailing further power and temperature increases, if they are
not limited by other measures. This effect was one of the physical causes
for the reactor accident in Chernobyl.
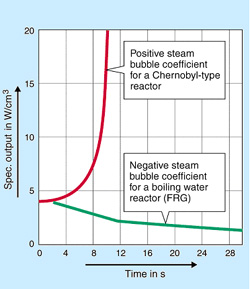
Evolution of reactor power under certain circum-stances
at positive and negative steam bubble coefficients
back
|
|

11 - 15 March 2018
Munich, Germany

30 September - 04 October 2018
Prague, Czech Republic |