
2005 ANNIVERSARY
20 YEARS OF DUKOVANY NPP IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC
Attachment to Press Release, information material
Twenty years ago Unit 1 of Dukovany NPP achieved
100% of rated power
This year the Czech nuclear industry celebrates
the twenty years of the day when the first of the four Dukovany’s
nuclear reactors was put into operation. The Nuclear Power Plant
(NPP) has been operated successfully since its commissioning,
as we can infer from the various national and international assessment
studies. In this period of anniversary, we ought to remember a
few significant dates.
Activity |
Date |
|
Start of reactor (first criticality) |
12th February 1985 |
|
Connection of turbogenerátor 1 to electric grid
|
24th February 1985 |
|
Connection of turbogenerátor 2 to electric grid
|
25th February 1985 |
|
100 % power |
26th March 1985 |
|
Start of Unit1 test operation |
3rd May 1985 |
|
Start of Unit1 commercial operation |
3rd November 1985 |
In the first year of operation, Dukovany NPP’s Unit 1 produced
2.4 billion KWh (TWh) and reached already 59.7 billion KWh (TWh)by
the end of 2004. Such amount of electricity would be sufficient
to supply all Czech households at their 2004 consumption level
for over 50 months.
In 2004 the Czech Republic’s total electricity
generation amounted to 84.3 billion KWh (TWh) and the share of
Dukovany NPP’s four Units was 16.2%. Together with the second
nuclear power plant of the country, Temelín NPP, the nuclear
share in total electricity production in the CR was 31.2%
About Dukovany NPP
History
The history of the Dukovany NPP dates back to 1970 when the former
Czechoslovakia and USSR signed an intergovernmental agreement
on the construction of two 1760 MW-nuclear power plants: one at
Jaslovské Bohunice in Slovakia and the second at Dukovany
in South Moravia. The Dukovany site was chosen because of the
nearby pumping hydro power plant in Dalesice with the balancing
reservoir Mohelno, both located on the Jihlava River. The hydro
system serves as a reservoir of cooling water for the nuclear
power plant.
Construction started in spring 1974
The construction of the NPP started in April 1974 but works were
suspended between 1976 and 1978. During this period, the design
was modified to fit the updated model of the VVER 440 –V213.
It was a very successful model of PWR reactors based on previous
Russian operating experience. The construction resumed in late
July 1978. The Czech national companies played a dominant role
in the construction of the NPP, and the manufacture and montage
of the equipment. 85% of all equipment was made in the Czechoslovakia
incl. reactors, steam-generators, turbines, etc. Companies such
as Skoda, Vitkovice and Kralovopolska were the main suppliers.
In full capacity in 1997
The pressure vessel was fitted in the structure of Unit 1 in November
1982 and the first criticality was achieved in February 1985.
Full power was achieved one month later. Next three Units were
subsequently commissioned in 1986 and 1987. Dukovany NPP reached
its full power of 1760 MW in July 1987. From the beginning of
its operation in 1985 to the end of 2004 the nuclear power plant
produced more than 238 billion KWh of electricity.
Nowadays
Over the whole period of its existence the Dukovany nuclear power
plant has featured high reliability, low rate of failures and
high safety. The major asset of the NPP is its contribution to
fighting climate change. It saves 17 million tons of CO2 a year
that would be otherwise released into the atmosphere by burning
11 million tons of coal in thermal power plants.
Nuclear is the cheapest power source
Nuclear reactors are operated at full power in the long term for
technical and economic reasons. Refuelling is performed once a
year and during this process approximately one fifth of the fuel
in the reactor is replaced. Since 1985 Dukovany NPP has changed
its fuel cycle from a 3-year cycle to a 5-year cycle and such
a change has reduced the volume of spent nuclear fuel by 5.3 tons
per Unit and per year. Such a modification has a significant economic
impact, resulting in cutting down fuel and storage costs. By the
end of 2004, Dukovany NPP had already saved more than 6 billion
CZK.
The advanced nuclear fuel with a 5-year cycle
was used at Dukovany NPP for the first time in 2003 in Unit 2
and later on in Units 1 and 4. This year, during the refuelling
of Unit 3, a completely new type of fuel is used for the first
time. This new fuel is characterised by reduction of Uranium 235
enrichment from 4.38% to 4.25% while maintaining the same fuel
assembly performance. Full transition of all four Dukovany Units
to the 5-year cycle will be accomplished by 2008. The Russian
company TVEL from Elektrostal factory (near Moscow) is a fuel
supplier for Dukovany NPP and the contract for the advanced fuel
is valid until 2011.
Nuclear Safety
Nuclear safety is a basic requirement of the Dukovany NPP operation.
It consists of a set of technical and organisational requirements,
aiming to ensure that the nuclear fission process and corresponding
release of radioactivity remain under control whatever the conditions.
Apart from nuclear safety, the power plant staff closely supervises
radiation safety. Radiation protection of human beings and of
the environment is ensured by protecting them against consequences
of ionising radiation and contact with radioactive substances.
Trained and highly qualified personnel
The outstanding operation of Dukovany NPP is not only a result
of designers, builders and manufacturers’ efforts. A highly
trained and qualified operation personnel is working at Dukovany
NPP. Every employee has to successfully go through health examinations
and regularly repeated psychological tests. Provided that he/she
fulfils all general qualification requirements, he/she is trained
in the Training Centre for the job. The most specific training
is provided for the licensed operators in main control rooms whose
expertise is examined every two years by a state examination committee
of top experts in the nuclear sphere. All in all 17% of workers
have trade and craft qualification, 49% high school qualification
and 33% university education.
Among the best performers
According to expert assessments, Dukovany NPP belongs to the best
performers among nuclear power plants worldwide. With regard to
a number of parameters and indicators, Dukovany NPP is above the
European average. Nuclear operators worldwide use performance
indicators of WANO (World Association of Nuclear Operators), based
on which Dukovany Units are in the first 20% of all reactors.
Public acceptance
The population living near the nuclear power plant is in favour
of nuclear power. According to an opinion poll, about 90 % of
the inhabitants living in a zone of 20 kilometres around the plant
back the operation of the nuclear power plant.
Future
As it was proved, the equipment of Dukovany NPP is capable of
being operated much longer than 30 years than initially designed.
Lifetime analysis and the aging of equipment showed that the lifetime
of the vital parts, particularly reactor vessels are from 70 to
140 years (on different Units). Other equipment is in a similar
shape. That is why the CEZ management decided to extend the lifetime
of Dukovany NPP to forty years, i.e. to 2025, at least. Based
on this decision a Harmonisation Programme has been developed
which sets up a number of particular projects (80) incl. equipment,
licensing, documentation, PR, personnel, competitiveness and management.
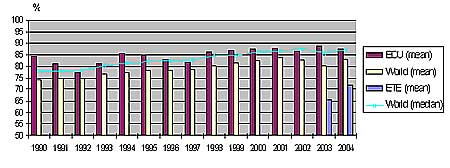
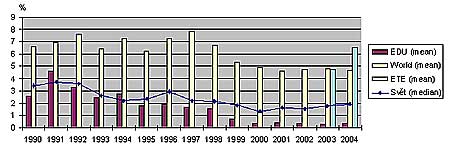
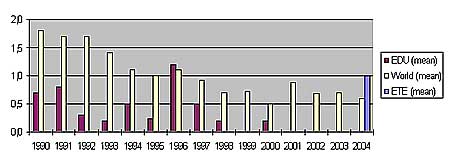
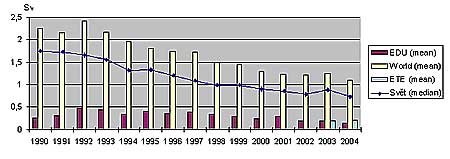
Performance Indicators (source WANO)
EDU = Dukovany NPP, ETE = Temelín NPP
Capacity Factor
Unplanned Capacity Loss Factor
Unplanned Automatic Scrams per 7,000 Hours Critical
Dukovany NPP has had no scrams for more than four years at any
of the four Units
Collective Radiation Exposure,
Man-Sieverts per unit
Dukovany NPP is Among Absolute Best NPPs Worlwide
Dukovany NPP - Basic Data
Significant Dates of Dukovany NPP Units
Stage / Unit |
1. |
2. |
3. |
4. |
Positioning of RPV |
26.12.1982 |
22.4.1983 |
27.2.1985 |
20.12.1985 |
First hydro-testing |
25.11.1983 |
6.4.1984 |
12.3.1986 |
2.9.1986 |
Minimum
controllable power |
12.2.1985 |
23.1.1986
|
28.10.1986 |
1.6.1987 |
First connection to the grid |
24.2.1985 |
30.1.1986
|
14.11.1986 |
11.6.1987 |
100% Power |
26.3.1985 |
21.2.1986 |
7.12.1986 |
3.7.1987 |
Test operation |
3.5.1985 |
20.3.1986 |
20.12.1986 |
19.7.1987 |
Commercial operation |
3.11.1985 |
21.9.1986
|
20.6.1987
|
19.1.1988 |
Dukovany NPP - Technical Parameters of Units
| Total installed capacity |
1760 MWe |
| Thermal efficiency |
32 % |
| Total efficiency |
29,2 % |
PRIMARY CIRCUIT |
Type of reactor |
PWR |
Number of reactors |
4 |
Fuel |
Slightly enriched Uranium U 235 |
Mass of fuel |
42 000 kg |
moderator |
Water with boric acid |
Number of controlled rods |
37 |
Number of fuel assemblies |
312 |
Steamgenerator type |
Horizontal, cylindrical |
Number of SG per Unit |
6 |
Pressuriser type |
cylindrical, vertical |
Number of pressurisers per Unit |
1 |
| SECONDARY CIRCUIT |
Turbine type |
3 parts, impulse, condensing turbine |
Turbine power |
220 MWe |
Rotation speed |
3000 rpm |
Number of TGs per Unit |
2 |
Generator |
Double-current g., synchronous atlernator |
Number of Generators per Unit |
2 |
Production History of Dukovany Units (GWh)
1985 - 2004
| |
1985 |
1986 |
1987 |
1988 |
1989 |
Unit 1 |
2397 |
2853 |
2768 |
2715 |
3156 |
Unit 2 |
|
2988 |
2855 |
2956 |
3216 |
Unit 3 |
|
308 |
3325 |
3193 |
2864 |
Unit 4 |
|
|
1753 |
2952 |
3182 |
Total in year |
2397 |
6149 |
10701 |
11816 |
12418 |
Total (GWh) |
2397 |
8546 |
19247 |
31063 |
43481 |
| |
1990 |
1991 |
1992 |
1993 |
1994 |
|
Unit 1
|
3180 |
2742 |
3173 |
3240 |
3279 |
Unit 2 |
3021 |
3098 |
2831 |
3257 |
3094 |
Unit 3 |
3187 |
3196 |
2918 |
3190 |
3344 |
Unit 4 |
3197 |
3096 |
3328 |
2940 |
3260 |
Total in year |
12585 |
12132 |
12250 |
12627 |
12977 |
Total (GWh) |
56066 |
68198 |
80448 |
93075 |
106052 |
|
1995 |
1996 |
1997 |
1998 |
1999 |
Unit 1 |
2966 |
3353 |
3296 |
3176 |
3092 |
Unit 2 |
3263 |
3019 |
3145 |
3423 |
3411 |
Unit 3 |
2690 |
3066 |
2905 |
3298 |
3464 |
Unit 4 |
3311 |
3412 |
3149 |
3281 |
3390 |
Total in year |
12230 |
12850 |
12494 |
13178 |
13357 |
| Total(GWh) |
118282 |
131132 |
143626 |
156804 |
170161 |
|
2000 |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
Unit 1 |
3553 |
3557 |
3492 |
3240 |
3241 |
Unit 2 |
3161 |
3341 |
3378 |
3474 |
3297 |
Unit 3 |
3413 |
3214 |
3487 |
3506 |
3530 |
Unit 4 |
3461 |
3482 |
2941 |
3535 |
3565 |
Total in year |
13588 |
13593 |
13299 |
13755 |
13632 |
Total(GWh) |
183748 |
197324 |
210623 |
224396 |
238028 |
|










