Electron volt
 scroll scroll 
Commonly used unit of energy in atomic and nuclear
physics. An electron volt is the kinetic energy gained by an electron
or other simply charged particles when passing through a voltage difference
of 1 Volt in vacuum. 1 eV is equal to the energy of 1.602 · 10-19 J. Derived greater units:
Kiloelectron volt (keV) = 1,000 eV
Megaelectron volt (MeV) = 1,000,000 eV
Gigaelectron volt (GeV) = 1,000,000,000 eV
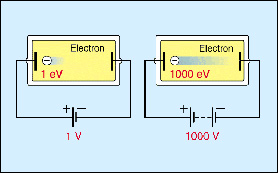
Illustration of the electron volt energy
unit
back
|
|

11 - 15 March 2018
Munich, Germany

30 September - 04 October 2018
Prague, Czech Republic |